Part 15: Neural Networks
Overview
Neural networks are powerful machine learning models inspired by how neurons work in the brain. They learn to recognize patterns by adjusting internal parameters (weights and biases).
Key Concepts:
- Neurons: mathematical functions that transform inputs
- Layers: groups of neurons (input, hidden, output)
- Activation functions: non-linear transformations (sigmoid, ReLU)
- Training: optimizing weights/biases to minimize prediction error
Import Libraries
Example Task: Digit Classification
Classify hand-written numbers (digits 0 through 9).
The original handwritten digits were pixelated into 64 pixels (8 x 8). Each observation consists of 65 numbers: the true digit and the darkness values of each of the 64 pixels. Darkness values range from 0 (white) to 16 (black).
Load and Explore the Digits Dataset
# Load the digits dataset
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.data # 8x8 images flattened to 64 features
y = digits.target # Digit labels 0-9
print(f"Digits Dataset:")
print(f" Total samples: {X.shape[0]:,}")
print(f" Features per sample: {X.shape[1]} (8×8 pixels)")
print(f" Classes: {len(np.unique(y))} (digits 0-9)")
print(f" Feature range: [{X.min():.1f}, {X.max():.1f}]")Digits Dataset:
Total samples: 1,797
Features per sample: 64 (8×8 pixels)
Classes: 10 (digits 0-9)
Feature range: [0.0, 16.0]Practice: Loading Data
Exercise 1 (with Gemini): Ask Gemini to “load the digits dataset from sklearn and print its shape”
Exercise 2 (on your own): Type from sklearn.datasets import load_digits then digits = load_digits() then print(digits.data.shape) and run it.
Visualize Sample Digits
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 10, figsize=(15, 4))
for digit in range(10):
idx = np.where(y == digit)[0][0]
axes[0, digit].imshow(X[idx].reshape(8, 8), cmap='gray_r')
axes[0, digit].axis('off')
idx2 = np.where(y == digit)[0][1]
axes[1, digit].imshow(X[idx2].reshape(8, 8), cmap='gray_r')
axes[1, digit].axis('off')
plt.suptitle('Two Examples Each of 0-9', fontsize=20, y=1.02)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Understanding Neural Networks: Simple Example
Generate customer data to predict purchase behavior:
- Input 1 (x1): Customer age (normalized)
- Input 2 (x2): Customer income (normalized)
- Target: 1 if customer purchases, 0 if not
Rule: customers usually purchase when age + income >= 0 (with noise)
Generate Customer Data
np.random.seed(42)
n_customers = 200
x1_age = np.random.uniform(-2, 2, n_customers)
x2_income = np.random.uniform(-2, 2, n_customers)
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, n_customers)
true_score = x1_age + x2_income + noise
y_purchase = (true_score >= 0).astype(int)
customer_data = pd.DataFrame({
'age_normalized': x1_age,
'income_normalized': x2_income,
'purchase': y_purchase
})
print("Customer Data Sample:")
print(customer_data.head())Customer Data Sample:
age_normalized income_normalized purchase
0 -0.501840 0.568127 1
1 1.802857 -1.663440 1
2 0.927976 -1.353485 1
3 0.394634 1.594217 1
4 -1.375925 0.425716 0Practice: Generating Data
Exercise 1 (with Gemini): Ask Gemini to “generate random data with numpy and create a pandas DataFrame”
Exercise 2 (on your own): Type x = np.random.uniform(0, 1, 10) then print(x) and run it.
Visualize Purchase Behavior
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
colors = ['red', 'blue']
labels = ['No Purchase', 'Purchase']
for i in [0, 1]:
mask = y_purchase == i
plt.scatter(x1_age[mask], x2_income[mask], c=colors[i], alpha=0.6,
label=labels[i], s=50)
x_line = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100)
y_line = -x_line
plt.plot(x_line, y_line, 'k--', linewidth=2,
label='Decision Boundary (age + income = 0)')
plt.xlabel('Age (normalized)')
plt.ylabel('Income (normalized)')
plt.title('Customer Purchase Behavior')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.show()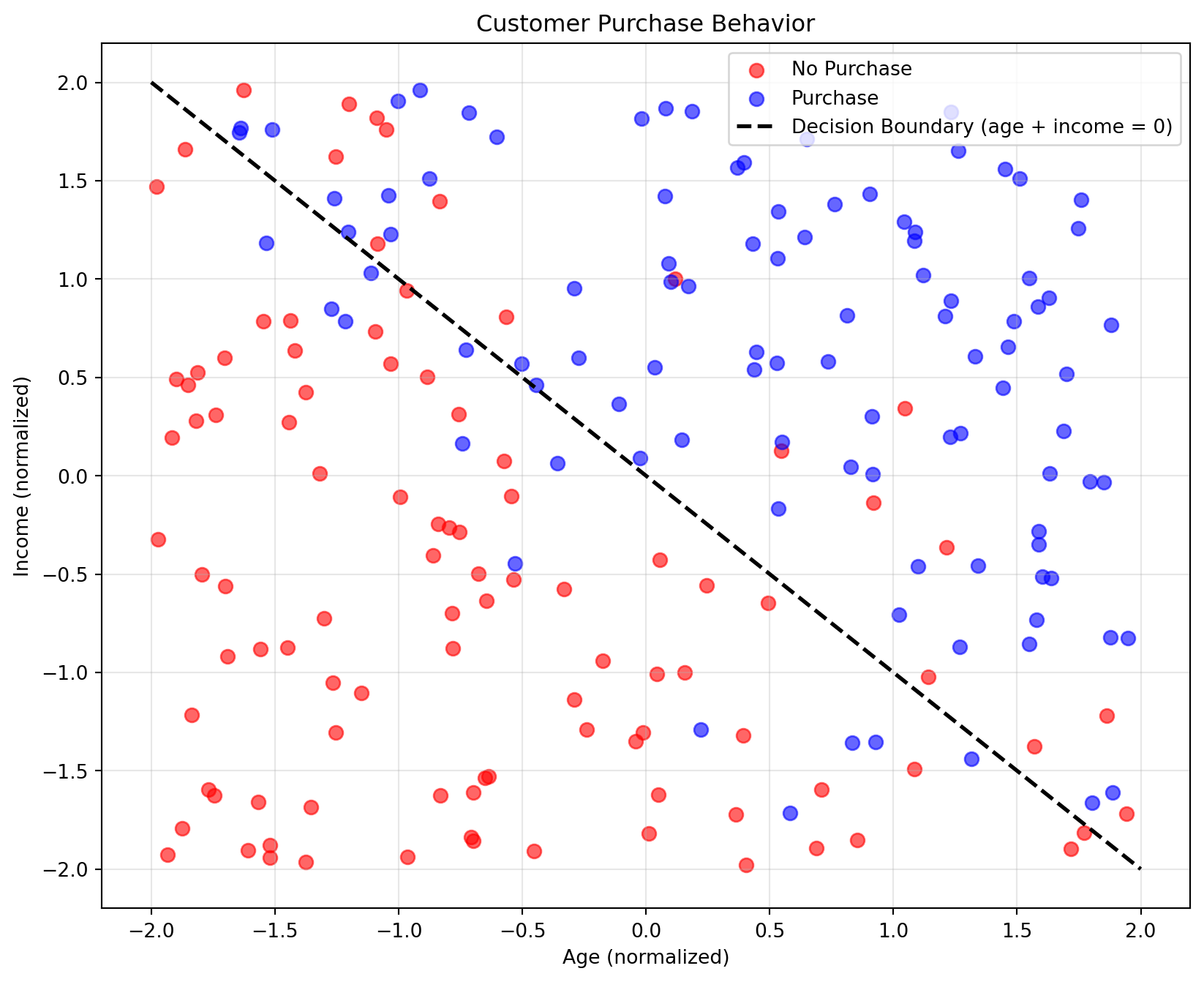
How Neurons Work
A neuron calculates a linear function then applies activation:
Linear Calculation: z = b + w1×x1 + w2×x2
- b = bias (intercept)
- w1, w2 = weights
Activation Functions:
- Sigmoid: h = 1/(1 + e^(-z)) outputs values in (0,1)
- ReLU: h = max(0, z) outputs values >= 0
The parameters (b, w1, w2) are learned from data during training.
Network Structure
Our simple network:
- Input layer: 2 inputs (x1, x2)
- Hidden layer: 3 neurons with sigmoid activation
- Output layer: 1 neuron with sigmoid activation
Parameters:
- Hidden layer: 3 biases + 3×2 weights = 9 parameters
- Output layer: 1 bias + 1×3 weights = 4 parameters
- Total: 13 parameters to optimize
Define Sigmoid Function
Practice: Sigmoid Function
Exercise 1 (with Gemini): Ask Gemini to “write a Python function that implements the sigmoid activation function”
Exercise 2 (on your own): Type def sigmoid(z): return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z)) then print(sigmoid(0)) and run it.
Example: Forward Propagation
# Network parameters (example values)
W1 = np.array([[0.5, 0.3], [-0.4, 0.6], [0.2, -0.3]])
b1 = np.array([0.1, -0.2, 0.3])
W2 = np.array([[0.7], [-0.5], [0.8]])
b2 = np.array([0.2])
# Example input
x_input = np.array([1.2, -0.8])
# Hidden layer calculation
z1 = W1 @ x_input + b1
h = sigmoid(z1)
# Output layer calculation
z2 = W2.T @ h + b2
y_hat = sigmoid(z2)[0]
print(f"Input: x1={x_input[0]}, x2={x_input[1]}")
print(f"Hidden: h1={h[0]:.3f}, h2={h[1]:.3f}, h3={h[2]:.3f}")
print(f"Output: y_hat={y_hat:.3f} ({y_hat:.1%} probability)")
print(f"Prediction: {'Purchase' if y_hat >= 0.5 else 'No Purchase'}")Input: x1=1.2, x2=-0.8
Hidden: h1=0.613, h2=0.239, h3=0.686
Output: y_hat=0.742 (74.2% probability)
Prediction: PurchasePractice: Forward Propagation
Exercise 1 (with Gemini): Ask Gemini to “explain how forward propagation works in a neural network with one hidden layer”
Exercise 2 (on your own): Type z = np.array([0.5, -0.3]) @ np.array([1.2, 0.8]) then print(z) and run it to practice matrix multiplication.
Summary
Neural Networks:
- Transform inputs through layers of neurons
- Each neuron applies weights, bias, and activation
- Parameters are optimized during training
- Can learn complex patterns in data
Next Steps:
- Use scikit-learn MLPClassifier for real applications
- Experiment with network architectures
- Try different activation functions
- Tune hyperparameters (learning rate, layers, neurons)